Welcome to the OpenEfficiency Initiative!
[intro_text]Performance Systems Development of New York, LLC (PSD), their supporting vendors and participating Program Administrators (PA) have been awarded a cooperative agreement with the Department of Energy to increase the range and depth of energy savings from whole building commercial energy efficiency (EE) programs through reduced program administrative costs and better alignment of program operations with private-sector market experience.[/intro_text]
Through delivery of a series of self-sustaining, whole building commercial energy efficiency program pilots built on an integrated open source platform, the OpenEfficiency Initiative (OEI) platform (OEP) will functionally integrate a range of federally funded tools.
Integrated Federally Funded Tools:
- Description: OpenStudio is DOE’s open-source “operating system” for building energy modeling. Started in 2008 with an EnergyPlus geometry creation plug-in for the 3D drawing tool SketchUp, OpenStudio has grown into a robust, full-featured software development kit (SDK) that automates many of the functions associated with creating energy models, modifying existing energy models to create design alternatives, running energy simulations, and collating, analyzing, and visualizing results from energy modeling experiments. OpenStudio automation dramatically reduces the effort required to build applications that use energy simulation and is aimed at growing and supporting the ecosystem of end-user simulation tools. By providing common infrastructure, OpenStudio allows third-parties to focus on adding their individual differentiating value and on serving their clients. OpenStudio allows DOE to realize its energy modeling market vision of “serving 50 energy modeling application vendors, not 50,000 energy modeling application end users.” DOE is consolidating its energy modeling application portfolio around OpenStudio.
- EDAPT – (DOE)
- Description: The Energy Design Assistance Program Tracker (EDAPT) tracks and manages projects, performs automated quality checks of energy model designs, and generates project documentation and reports for commercial buildings. The ultimate goal of this project is to develop cost control best practice guidance that key industry users (building owners, architects, designers, energy champions, etc.) can incorporate into their everyday workflows. This project also includes compiling and disseminating data about the cost effectiveness of net zero energy (NZE) buildings that use innovative technologies and design approaches. By demonstrating how to combine NZE technologies and design approaches into an overall efficiency package that can be implemented at minimal incremental capital cost, this project will help expand the domain of NZE design and construction.
- Asset Score – (DOE)
- Description: The U.S. Department of Energy’s Building Energy Asset Score (Asset Score) is a national standardized tool for assessing the physical and structural energy efficiency of commercial and multifamily residential buildings. The Asset Score generates a simple energy efficiency rating that enables comparison among buildings, and identifies opportunities to invest in energy efficiency upgrades. It is available for voluntary use and is 100% free to use.
- SEED – (DOE)
- Description: The Standard Energy Efficiency Data (SEED) Platform™ is an open source software application that helps organizations easily manage data on the energy performance of large groups of buildings. Users can combine data from multiple sources, clean and validate it, and share the information with others. The software application provides an easy, flexible, and cost-effective method to improve the quality and availability of data to help demonstrate the economic and environmental benefits of energy efficiency, to implement programs, and to target investment activity.
- Portfolio Manager – US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Description: EPA created ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager® to measure and track energy and water consumption, as well as greenhouse gas emissions. Benchmark the performance of one building or a whole portfolio of buildings.
- Automated Measurement & Verification – Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL)
- Description: Streamlined or Automated M&V strategies provide a means to estimate savings for whole-building-focused energy efficiency approaches. There is growing recognition that whole-building-focused approaches to energy efficiency hold great promise in realizing deep and persistent energy savings in commercial buildings. Owners, property and facility managers, and utility incentive programs are increasingly adopting and piloting multi-measure strategies that move beyond traditional component-based or one-time commissioning or retrofit interventions; the industry is seeing a movement toward continuous energy improvement practices that may include efforts such as ongoing commissioning, strategic energy management, and operational optimization, as well as retrofits and the implementation of advanced control and information technologies.
- Building Energy Data Exchange Specification BEDES – (LBNL)
- Description: The Building Energy Data Exchange Specification (BEDES, pronounced “beads”) is a dictionary of terms and definitions commonly used in tools and activities that help stakeholders make energy investment decisions, track building performance, and implement energy efficient policies and programs. An ecosystem of BEDES Compliant software will facilitate the exchange of information on building characteristics and energy use.
- BuildingSync – National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
- Description: BuildingSync® is a standardized language for commercial building energy audit data that software developers can use to exchange data between audit tools. Taking the form of an XML schema, BuildingSync can be required by building owners and audit program managers to allow data analysis and aggregation across multiple buildings in order to evaluate program performance and analyze trends.
Improved PA Cost-Effectiveness For Program Models:
- Whole Building
- Local Government Benchmarking
- Auditing
The overall intent is to make regulated commercial building energy programs easier and more cost-effective for administrators, with simplified and automated processes for practitioners and building owners.
[break]
[white_box]
Training Programs
Software overview webinars will be held biweekly for the next few months to familiarize the OEI Partner Network with all proposed software solutions.
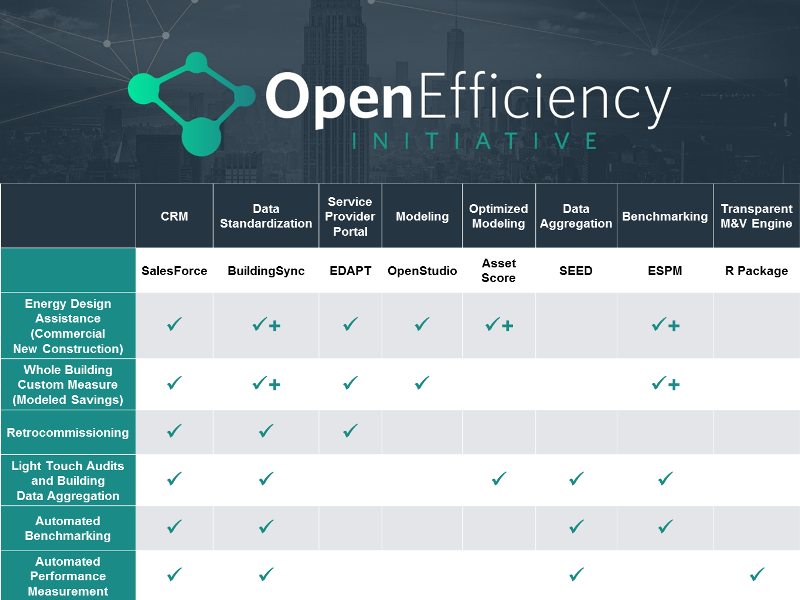
The following matrix provides our current understanding of the relationships of program designs to the various tools. We will be providing an introduction to purpose and capabilities of each of these tools as they relate to our project in a series of webinars. These webinars are currently in development.